What is BHP? Is BHP different from HP?
3349 Views
Learn what sets brake horsepower (bhp) and horsepower (hp) apart. Find out why these terms measure a vehicle’s power differently.

Whether you own a vehicle or not, chances are you have come across the term Horsepower at some point. HP is a metric frequently used in car advertisements and commonly discussed by individuals in machine shops and car enthusiasts. However, have you ever wondered about the term Brake Horsepower, or BHP? Let's delve into the disparity between these two measurements.
What is Horsepower?
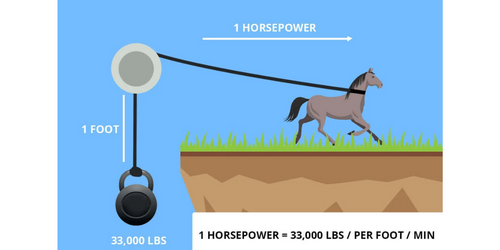
What does horsepower mean? It is a numerical value employed to quantify the power of an engine and is frequently abbreviated as hp. In simpler terms, it represents the engine's capacity for performing work.
A car's speed relies on more than just raw power, as there are other scientific factors at play. However, power has a significant impact on the overall performance of a car, particularly its acceleration ability.
What is BHP?
Brake horsepower or bhp refers to the horsepower of the car after taking into consideration friction between a car’s tyres and the road.
In other words, brake horsepower accounts for the power loss due to friction, which is why brake horsepower is always less than a car’s horsepower. Thus, bhp and hp do not mean the same.
Understanding replica measurements:
While the term "horsepower" is commonly used to refer to the metric measurement, it goes by different names in other regions. Additionally, there exist various equivalent measurements, including:
PS: This abbreviation derives from the German term "pferdestarke," which literally translates to horsepower. PS is the most commonly used measurement in Europe and is exactly equivalent to horsepower.
CV: Similar to PS, CV is a direct equivalent of horsepower. It is a French acronym standing for "chevaux-vapeur."
kW: This abbreviation stands for kilowatt and is predominantly used in Europe to express power outputs of electric cars. Approximately 1 kilowatt is equivalent to 1.3 horsepower.
BHP vs HP
Brake horsepower (bhp) is generally lower than horsepower (hp) because it takes into consideration power losses caused by friction and other inefficiencies. As a result, bhp and hp should not be used interchangeably when discussing a car's power output.
The disparity between the two measurements is minimal on a 1:1 basis. One horsepower is approximately equal to 0.99 brake horsepower. However, when scaled up, differences become noticeable. For instance, a car with 300 horsepower would be equivalent to 296 brake horsepower.
While manufacturers now commonly publish power figures in horsepower, the usage of bhp as a measurement still persists in some traditional car magazines. Therefore, when comparing a car's performance, it is important to ensure a like-for-like comparison rather than comparing hp and bhp.
Ultimately, the choice of preferred measurement is not of great significance, although horsepower may sound slightly more impressive when boasting to friends.
How is BHP & HP measured?
To quantify the power of an engine, a device known as a dynamometer, or dyno, is utilized. The power measurement process involves distinguishing between two types: metric horsepower (hp) and brake horsepower (bhp).
Metric horsepower is gauged by observing the crankshaft as it accelerates to its maximum rotational speed. On the other hand, brake horsepower is determined by spinning the crankshaft up to its maximum speed and allowing it to decelerate naturally until it comes to a complete stop. This methodology takes into account the influence of friction on the engine's power output.