Bike Engines 101: A Guide to the Different Types and Their Difference
1560 Views
Learn about the different types of bike engines, how they work, and what they offer. Find out how to choose the best bike engine for your needs and preferences.

If you are a bike enthusiast, you might have wondered what makes different bikes perform differently. The answer lies in the type of engine that powers them. The engine is the heart of a bike, and it determines its speed, acceleration, fuel efficiency and sound.
There are different types of engines that are used in bikes, and each one has its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article, I will explain the main types of bike engines and their pros and cons.
By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of how bike engines work and what type of engine suits your needs and preferences.
Single-cylinder engine:

This type of engine has only one cylinder and works best on small cc bikes. It is cheap to maintain and fix if something goes wrong. It also produces high torque at low revs, which makes it suitable for off-road and commuter bikes. Example: Splendor, Platina and even Yamaha R15.
Pros: compact size, lightweight, inexpensive, high torque at low revs.Cons: high vibrations, difficult balancing.
Technical Explanation: A single-cylinder engine is also known as a thumper or a single. It has a simple design with one piston, one connecting rod, one crankshaft and one spark plug. It uses a four-stroke cycle or a two-stroke cycle to convert fuel into power. A four-stroke cycle consists of four phases: intake, compression, power and exhaust. A two-stroke cycle consists of two phases: compression/power and exhaust/intake. A single-cylinder engine has a high power-to-weight ratio but also suffers from high vibrations and poor balance due to the uneven firing intervals.
Twin-cylinder engine:

This type of engine has two cylinders that share a common crankshaft. There are different subtypes of twin-cylinder engines, such as parallel-twin, V-twin, L-twin and boxer engine. They are generally found in medium and high displacement models. They offer more power, comfort and fluid operation than single-cylinder engines, but also have higher vibrations and cost.
Pros: more power, comfort, fluid operation.Cons: higher vibrations, cost.
Technical Explanation: A twin-cylinder engine is also known as a twin or a parallel twin. It has a complex design with two pistons, two connecting rods, one crankshaft and two spark plugs. It uses a four-stroke cycle or a two-stroke cycle to convert fuel into power. A twin-cylinder engine has a lower power-to-weight ratio than a single-cylinder engine but also has lower vibrations and better balance due to the even firing intervals. There are different configurations of twin-cylinder engines based on the angle between the cylinders:
A parallel-twin engine has two cylinders arranged in a line along a common crankshaft. The pistons move in sync with each other. Examples are Kawasaki Ninja 650 and RE Interceptor 650.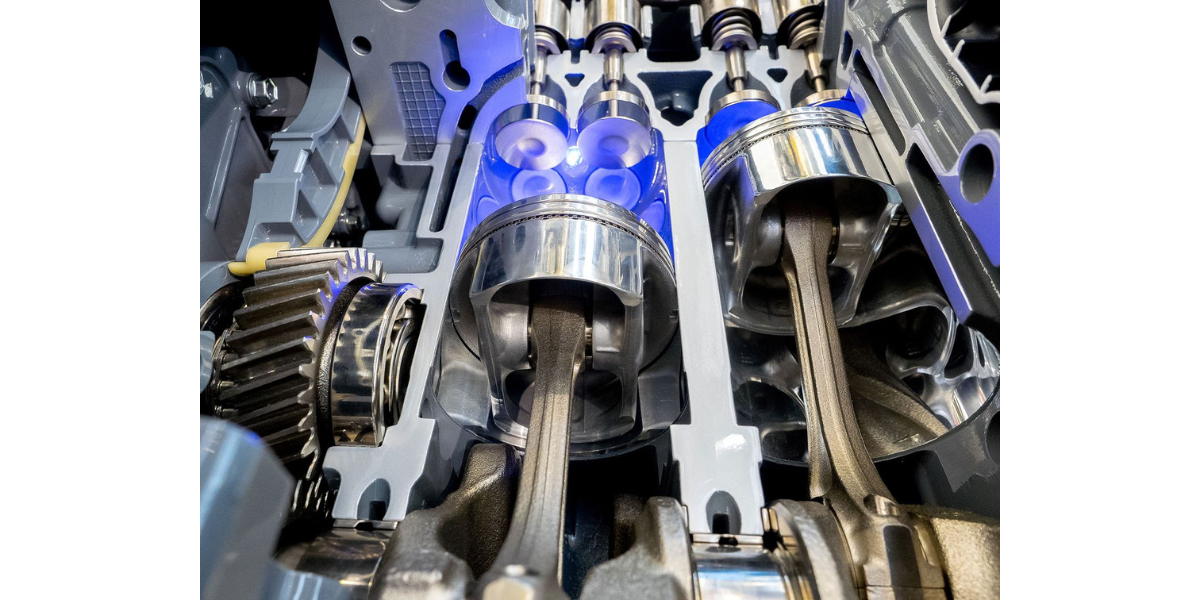
A V-twin engine has two cylinders arranged in a V shape along a common crankshaft. The pistons move at different times with each other. Examples are Harley-Davidson Sportster and Keeway V302C.
An L-twin engine has two cylinders arranged in an L shape along a common crankshaft. The pistons move at different times with each other but have a 90-degree angle between them. Examples are Ducati Monster and Hyosung GT650R.
A boxer engine has two cylinders arranged in an opposite direction along a common crankshaft. The pistons move away from each other at the same time. Examples are BMW R1200GS and Honda Gold Wing.
Triple-cylinder engine:
This type of engine has three cylinders arranged in a line or a triangle along a common crankshaft. It combines the advantages of both single-cylinder and twin-cylinder engines, such as high torque at low revs, smooth operation, high performance and good balance. It also has less vibrations and weight than four-cylinder engines. However, it is more expensive and complex than single-cylinder and twin-cylinder engines.
Pros: high torque at low revs, smooth operation, high performance, good balance.Cons: more expensive, complex.
Technical Explanation: A triple-cylinder engine is also known as a triple or a triples. It has a sophisticated design with three pistons, three connecting rods, one crankshaft and three spark plugs. It uses a four-stroke cycle to convert fuel into power. A triple-cylinder engine has a higher power-to-weight ratio than a twin-cylinder engine but also has lower vibrations and better balance due to the shorter firing intervals. There are different configurations of triple-cylinder engines based on the arrangement of the cylinders:
An inline-triple engine has three cylinders arranged in a line along a common crankshaft. The pistons move in sync with each other. Examples are Triumph Street Triple and Yamaha MT-09.
A radial-triple engine has three cylinders arranged in a triangle along a common crankshaft. The pistons move at different times with each other. Examples are MV Agusta Brutale and Benelli TNT 899.
Four-cylinder engine:
This type of engine has four cylinders arranged in a line or a V along a common crankshaft. It is the most powerful and refined type of bike engine, offering high speed, acceleration and smoothness. It also has low vibrations and good balance. However, it is also the heaviest, most expensive and most complicated type of bike engine. It also consumes more fuel than other types of engines.
Pros: high speed, acceleration, smoothness, low vibrations, good balance.Cons: heavy, expensive, complicated, high fuel consumption.
Technical Explanation: A four-cylinder engine is also known as a four or a fours. It has an advanced design with four pistons, four connecting rods, one crankshaft and four spark plugs. It uses a four-stroke cycle to convert fuel into power. A four-cylinder engine has the highest power-to-weight ratio of all bike engines but also has the lowest vibrations and best balance due to the very short firing intervals. There are different configurations of four-cylinder engines based on the angle between the cylinders:
An inline-four engine has four cylinders arranged in a line along a common crankshaft. The pistons move in sync with each other. Examples are Honda CBR1000RR and Suzuki GSX-R1000.
A V-four engine has four cylinders arranged in a V shape along a common crankshaft. The pistons move at different times with each other. Examples are Honda VFR1200F and Aprilia RSV4.
A flat-four engine has four cylinders arranged in an opposite direction along a common crankshaft. The pistons move away from each other at the same time. Examples are Honda CB750 and BMW K1200RS.
Straight six engine:
This type of engine has six cylinders arranged in a line along a common crankshaft. It is the rarest and most exotic type of bike engine, offering unmatched power, smoothness and sound. It also has very low vibrations and excellent balance. However, it is also the largest, heaviest, most expensive and most impractical type of bike engine. It also consumes a lot of fuel and space.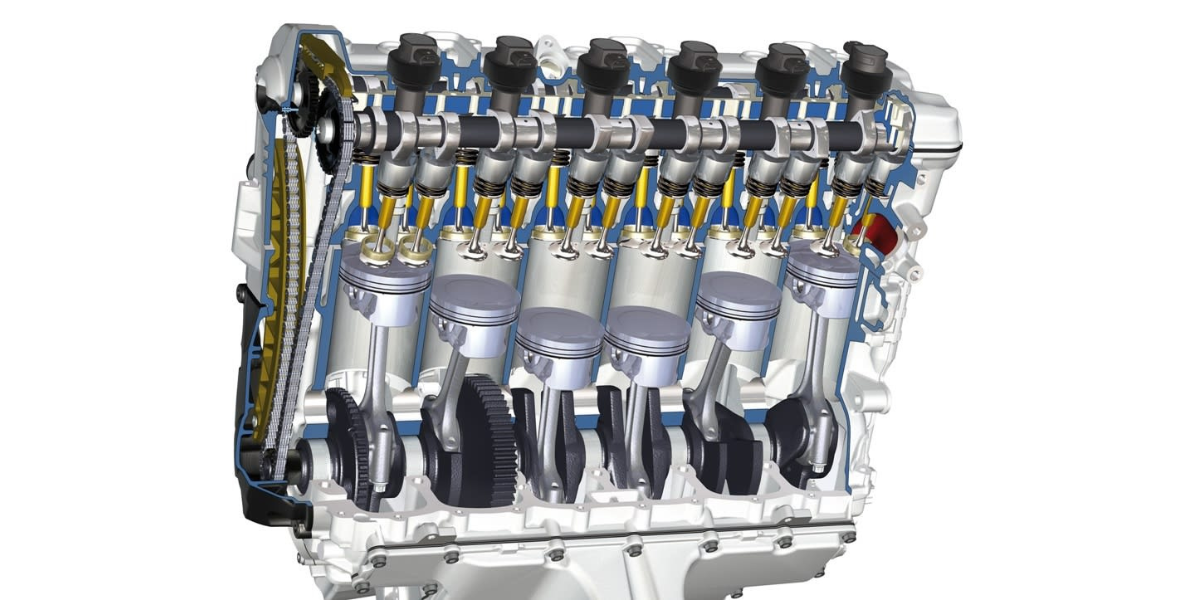
Pros: unmatched power, smoothness, sound, low vibrations, excellent balance.
Cons: large, heavy, expensive impractical high fuel consumption space.
Technical Explanation: A straight six engine is also known as a six or a sixes. It has an exceptional design with six pistons, six connecting rods, one crankshaft and six spark plugs. It uses a four-stroke cycle to convert fuel into power. A straight six engine has an extraordinary power-to-weight ratio but also has the lowest vibrations and best balance of all bike engines due to the extremely short firing intervals. However, it is also the most difficult to fit in a bike frame due to its length and width. Examples of bikes with straight six engines are Honda CBX1000 Kawasaki Z1300 BMW K1600GT.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, bike engines are diverse and fascinating machines that offer different benefits and drawbacks. Different bike makers have their own preferences for the types of engines they use. They have their own reasons for choosing a certain kind of engine for each bike model. So when you shop for bikes, you’ll notice some patterns among each brand.
This also means that if you want a specific kind of engine, you might have to pick a certain model or brand.
Depending on your riding style, budget and taste, you can choose from various types of engines that range from simple and economical to powerful and sophisticated. The type of engine you choose will affect your bike’s performance, fuel efficiency and sound. I hope this article has helped you learn more about the different types of bike engines and how they affect your riding experience.
Thank you for reading and happy riding!