How do Hydrogen cars work & are they the future?
1378 Views
Discover the inner workings of hydrogen cars and their potential as a game-changing mode of transportation. Explore how it works, the future possibilities, the pros and cons, and find answers to frequently asked questions about this innovative technology.

In recent years, there has been a growing interest in finding alternative and sustainable fuel sources to power our vehicles. One such solution gaining traction is the hydrogen car, which harnesses the incredible potential of hydrogen as a clean and efficient energy carrier.
Hydrogen cars, also known as H2 cars, utilize hydrogen fuel as their power source, offering energy-efficient alternatives to conventional gasoline-powered vehicles. These cars rely on hydrogen fuel cells, which generate electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen, ultimately propelling the vehicle forward.
Leading automobile manufacturers like Toyota are actively investing in hydrogen as a future fuel option, aiming to provide a cleaner alternative to gas or electric-powered vehicles. Currently, approximately 11,000 hydrogen cars are in operation worldwide, with the United States, Japan, China, and South Korea making significant investments in the future of hydrogen as a sustainable fuel source.
Why choose hydrogen? This question has spurred considerable interest and research. Toyota, in particular, is at the forefront of hydrogen vehicle development, striving to make these vehicles accessible and affordable in the future. To understand the inner workings of hydrogen fuel cells, explore the advantages and disadvantages of H2 vehicles, and gain further insights, continue reading or refer to our accompanying infographic for a visual representation.
The Basics: Hydrogen as a Fuel
At its core, a hydrogen car utilizes hydrogen gas (H₂) as its primary fuel source. Hydrogen, the most abundant element in the universe, can be produced through various methods such as electrolysis, where water is split into hydrogen and oxygen using an electric current. This process can be powered by renewable energy sources like solar or wind, making hydrogen a potentially green fuel option.
The Fuel Cell: Powering the Vehicle: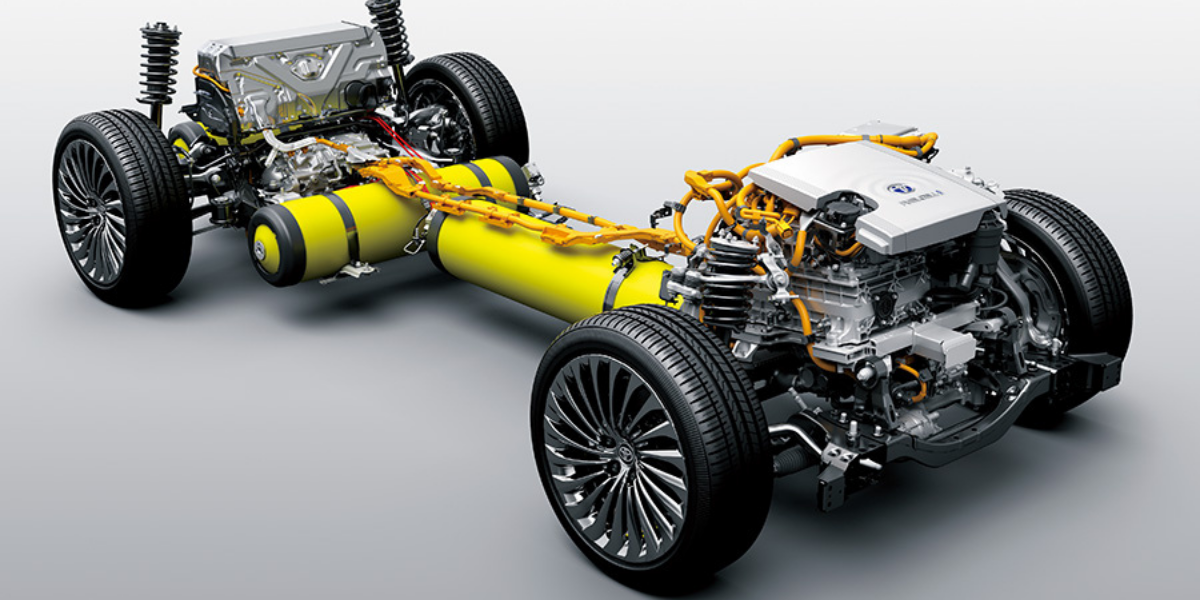
The heart of a hydrogen car is the fuel cell, a device that converts hydrogen gas and oxygen from the air into electricity, with water being the only byproduct. A fuel cell consists of three main components: an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte.
As hydrogen gas flows over the anode, it splits into protons and electrons. The protons pass through the electrolyte, while the electrons take an external route, creating an electric current that can be used to power the vehicle's electric motor.
Storing Hydrogen: The Challenge
One of the key challenges in the widespread adoption of hydrogen cars lies in the safe and efficient storage of hydrogen. Due to its low density, hydrogen gas must be compressed or liquefied to be stored effectively.
Compressed hydrogen is stored in high-pressure tanks, while liquid hydrogen is kept at extremely low temperatures. Both methods require specialized infrastructure and present unique engineering hurdles that automakers are actively working to overcome.
Advantages of Hydrogen Cars:

Hydrogen cars offer several advantages over conventional gasoline or electric vehicles. Firstly, hydrogen is highly efficient as an energy carrier, providing more energy per unit weight compared to other fuels.
Additionally, refuelling a hydrogen car takes a similar amount of time as filling up a conventional gasoline vehicle, alleviating concerns about range anxiety. Moreover, hydrogen cars emit only water vapor, making them a truly zero-emission transportation option, thus contributing to a cleaner and greener future.
Challenges of Hydrogen Cars in India:
While hydrogen fuel cell vehicles hold considerable potential, there are several hurdles to overcome before they can become a practical and widely adopted option for consumers. One significant challenge is the high cost associated with producing and storing hydrogen fuel. The current methods of hydrogen production are expensive and energy-intensive, making it difficult to compete with traditional gasoline engines in terms of cost-effectiveness.
Another obstacle lies in the limited infrastructure for refuelling hydrogen vehicles. With only a few dozen hydrogen refuelling stations currently available in the United States, finding convenient refuelling options can be challenging for drivers.
Furthermore, hydrogen cars face competition from more readily available and cheaper alternatives, such as electric cars. The lower cost and greater accessibility of electric vehicles present a significant challenge for the wider acceptance of hydrogen fuel cell technology.
The Future of Hydrogen Cars:
The future of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles holds several promising prospects. Technological advancements are driving greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness in hydrogen production and storage, while innovative fuel cell designs are paving the way for lighter and more affordable vehicles.
Governments worldwide are demonstrating significant commitment to hydrogen fuel cell technology. Countries like Japan and Germany have set ambitious targets for the adoption of hydrogen-powered vehicles. In the United States, the Biden administration has proposed a substantial $15 billion investment in hydrogen fuel cell technology as part of its clean energy transition plan.
Furthermore, the growing focus on environmental benefits is amplifying the importance of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. As governments and consumers strive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, the renewable energy sector is witnessing remarkable growth. With the increasing prevalence of clean energy sources like wind and solar power, hydrogen production can be powered sustainably, making hydrogen fuel cells an even more environmentally friendly transportation option.
India’s plan for Hydrogen Cars:
In a recent significant budget announcement in 2023, the Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman unveiled the National Green Hydrogen Mission, allocating a budget of Rs 19,700 crore.
This ambitious project positions India with the goal of becoming a global leader in hydrogen production, recognizing hydrogen as a crucial solution for future energy requirements. India has also made a commitment to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2070. The National Green Hydrogen Mission sets a target of producing 5 million metric tons (MMT) of hydrogen annually by 2030.
Pros:
Environmentally Friendly: Hydrogen cars produce zero emissions, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
Fuel Efficiency: Hydrogen is a highly efficient energy carrier, offering longer driving ranges and reduced refueling frequency.
Quick Refueling: Refueling a hydrogen car takes a similar amount of time as refueling a conventional gasoline vehicle, alleviating range anxiety.
Versatility: Hydrogen can be produced from renewable energy sources, enhancing its potential integration with existing renewable energy infrastructure.
Potential for Energy Storage: Hydrogen can be used as an energy storage medium, supporting the utilization of excess renewable energy.
Cons:
Limited Infrastructure: The availability of hydrogen refueling stations is currently limited, hindering widespread adoption.
Cost and Complexity: Hydrogen cars tend to be more expensive due to complex technologies and infrastructure involved in production, storage, and transportation.
Storage and Safety Concerns: Hydrogen requires specialized safety measures, addressing concerns regarding leakage, transportation, and storage.
Limited Vehicle Models: The selection of hydrogen car models on the market is relatively limited compared to gasoline or electric vehicles.
Energy Efficiency of Production: Hydrogen production can be energy-intensive, especially if non-renewable sources are used.
Frequently Asked Questions on Hydrogen cars
1. Are Hydrogen Cars the future?
By 2030, we envisage hydrogen to be in use not only in cars, but across a range of transport modes, including heavy goods vehicles, buses and rail, along with early stage uses in commercial shipping and aviation. This has to do with the abundance of resources to produce Hydrogen.
2. Are hydrogen cars better than electric cars?
The weight of a hydrogen fuel cell system, including the hydrogen tank, is significantly lighter compared to a battery. As a result, the electric motor in a hydrogen car requires less power to propel the vehicle due to its reduced weight. This makes it more efficient, lighter and thus, faster than Electric cars
3. Can Hydrogen Cars explode?
Hydrogen used in the fuel cells is a very flammable gas and can cause fires and explosions if it is not handled properly.
4. Why are hydrogen cars not popular?
The primary advantage of hydrogen vehicles is their emission-free nature compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) counterparts. However, the majority of energy used in the production of hydrogen, which is not readily available and must be extracted or created using existing resources, is currently derived from natural gas.
5. How safe are Hydrogen Cars?
Contrary to what may seem, hydrogen as a fuel for cars is actually safer than gasoline. Due to its lighter-than-air property, in the event of a localized leak in the tank, hydrogen forms a narrow, vertical flame that does not generate high temperatures and does not spread easily.