What is ADAS & How it works?
10895 Views
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), also known as ADAS, employ a human-machine interface to enhance a driver's responsiveness to road hazards.

In recent years, the Indian automotive market has witnessed a significant transformation of safety features incorporated in newer car models. And speaking of safety features, integration of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) cannot be left behind. Well, it isn’t.
ADAS represents a groundbreaking leap forward in automotive technology, employing a range of sensors, cameras, and radar systems to enhance safety, convenience, and overall driving experience.
In this article, we will delve into the ‘what's’ and 'how's' of ADAS, by exploring its various features, backed by factual research, and shed light on how it is revolutionizing the way we drive.
What is ADAS?
Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are technological features that aim to enhance driving safety. These systems utilize a human-machine interface to improve a driver's ability to react to road dangers.
ADAS systems increase safety and response times by providing early warnings and employing automated systems. Some vehicles come equipped with standard ADAS features, while aftermarket options are available to personalize a vehicle with additional ADAS capabilities.
The goal of ADAS is to create a symbiotic relationship between the driver and the vehicle, leveraging technology to enhance confidence and safety on the road. These systems assist in collision avoidance, provide lane departure warnings, and offer features like adaptive cruise control.
By integrating advanced sensors, cameras, and processing algorithms, ADAS adds an extra layer of protection to the driving experience. The effectiveness of ADAS is backed by research and testing, ensuring high safety standards.
ADAS technology continues to evolve, with ongoing research focused on introducing more sophisticated features. Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning have the potential to further enhance ADAS capabilities.
The popularity of safety systems in vehicles has significantly risen due to technological advancements and the proliferation of automation initiatives. A wide range of available systems showcases this trend, and some notable examples include:
1. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC):
ACC is a standout feature in ADAS that helps drivers maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead. By utilizing radar or camera-based sensors, ACC adjusts the vehicle's speed accordingly. ACC can prove highly beneficial in India, where dense traffic and varying speeds on the highways are quite common.
2. Anti-Lock Braking System:
In the context of ADAS, ABS works in conjunction with other safety features to enhance overall braking performance and control. When the driver applies the brakes, the ABS continuously monitors the rotational speed of each wheel. If it detects that one or more wheels are about to lock up or lose traction, the ABS modulates the brake pressure to that particular wheel or wheels
3. Lane Departure Warning (LDW) & Lane Keep Assist (LKA):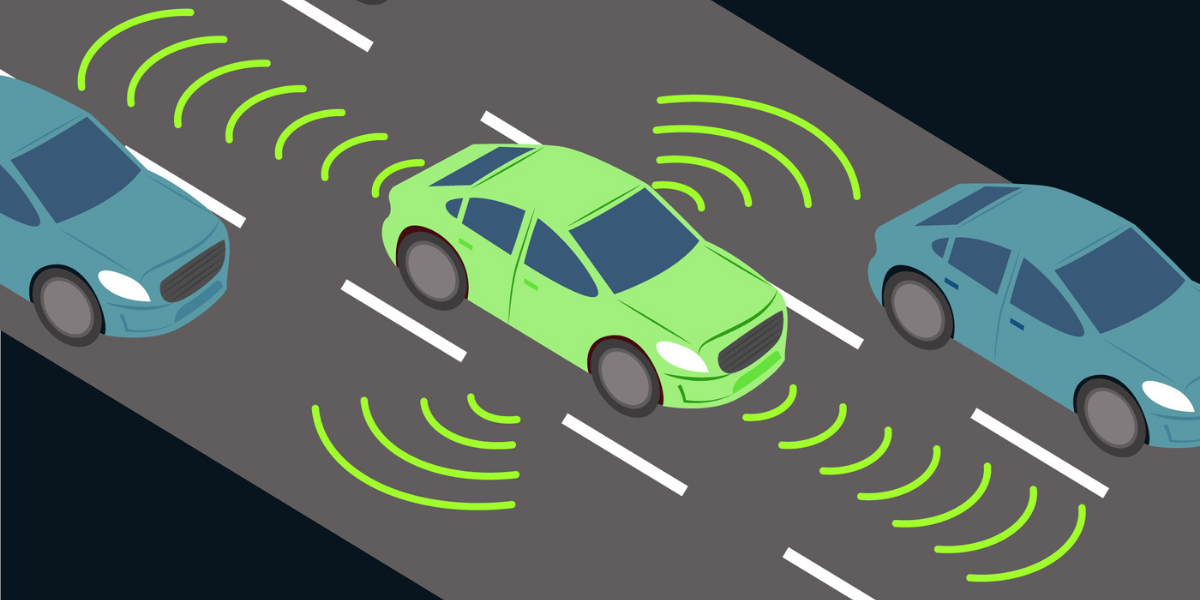
The LDW alerts drivers if their vehicle deviates from its lane, ensuring they stay within their designated path. Whereas, LKA further assists by providing gentle steering inputs to help drivers maintain their lane. Indian roads specifically, are prone to frequent lane changes, uneven road markings, and crowded traffic. However, these features will help you reduce the risk of lane departure-related accidents.
4. Forward Collision Warning (FCW) & Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB):
The FCW & AEB are paramount ADAS features that are capable of addressing the discrete challenges of Indian road traffic. FCW uses sensors to detect potential collisions and warns the driver in advance. AEB takes it a step further by automatically applying the brakes if the driver fails to respond.
5. Blind Spot Detection (BSD):
Here is a feature that will comfort you from the frequent lane changes and overtaking manoeuvres. BSD uses sensors to monitor blind spots and alerts the driver of vehicles in adjacent lanes. This technology enhances safety by minimizing the risk of accidents caused by insufficient visibility and assists drivers in making informed decisions when changing lanes.
6. Traffic Sign Recognition (TSR):
By utilizing cameras or image processing algorithms, TSR detects and interprets traffic signs, displaying relevant information to the driver. This feature ensures drivers remain aware of speed limits, no-overtaking zones, adhering to more traffic rules, and promoting safer driving practices on Indian roads.
7. Traction Control:
Traction control in ADAS works in conjunction with other features, such as stability control systems and anti-lock braking systems (ABS). These integrated systems work together to optimize vehicle stability, prevent skidding, and ensure safe and controlled driving even in challenging road conditions.
8. Automatic High Beams (AHB):
Automatic High Beams (AHB) are valuable on Indian roads, which often lack well-lit areas and encounter a mix of vehicles with varying headlight usage. AHB technology automatically adjusts the headlights between high and low beams, optimizing visibility for the driver without causing inconvenience to other road users.
How does ADAS work?
Most newer vehicles are equipped with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) as a standard feature. These systems are continually updated by car manufacturers as they introduce new models and advanced functionalities. ADAS relies on various data sources to provide valuable safety features. One important data source is automotive imaging, which uses advanced sensors to create a detailed 360-degree view, allowing the system to accurately perceive objects in three dimensions. This imaging technology performs exceptionally well in challenging weather conditions and low-light situations, providing real-time data to enhance safety.
To further enhance its capabilities, ADAS can incorporate LiDAR (light detection and ranging). LiDAR adds more cameras and sensors that enable the system to create 3D representations of the surroundings. It can accurately differentiate between stationary and moving objects, making it particularly useful in blind-spot monitoring and situations with poor lighting conditions.
In addition to the primary vehicle platform, ADAS can also leverage data inputs from other sources. This includes communication between vehicles (V2V) or between vehicles and infrastructure (V2X) using technologies like WiFi. These additional data sources enable ADAS to access real-time information and enhance safety and efficiency on the road.
As ADAS technology continues to evolve, wireless network connectivity and the utilization of V2V and V2X data will play a significant role in advancing its capabilities. These advancements will not only improve safety but also provide additional value to drivers.
And finally
It is important to note that ADAS features may vary across vehicle models and manufacturers. Furthermore, while ADAS technology offers numerous benefits, it is crucial for drivers to understand that these systems are designed to assist, not replace, their attention and responsibility. Drivers should remain vigilant, follow traffic laws, and be prepared to take control of the vehicle when necessary.